BEE (Basic Electrical Engineering)
₹599.00
₹149.00
-
Introduction
-
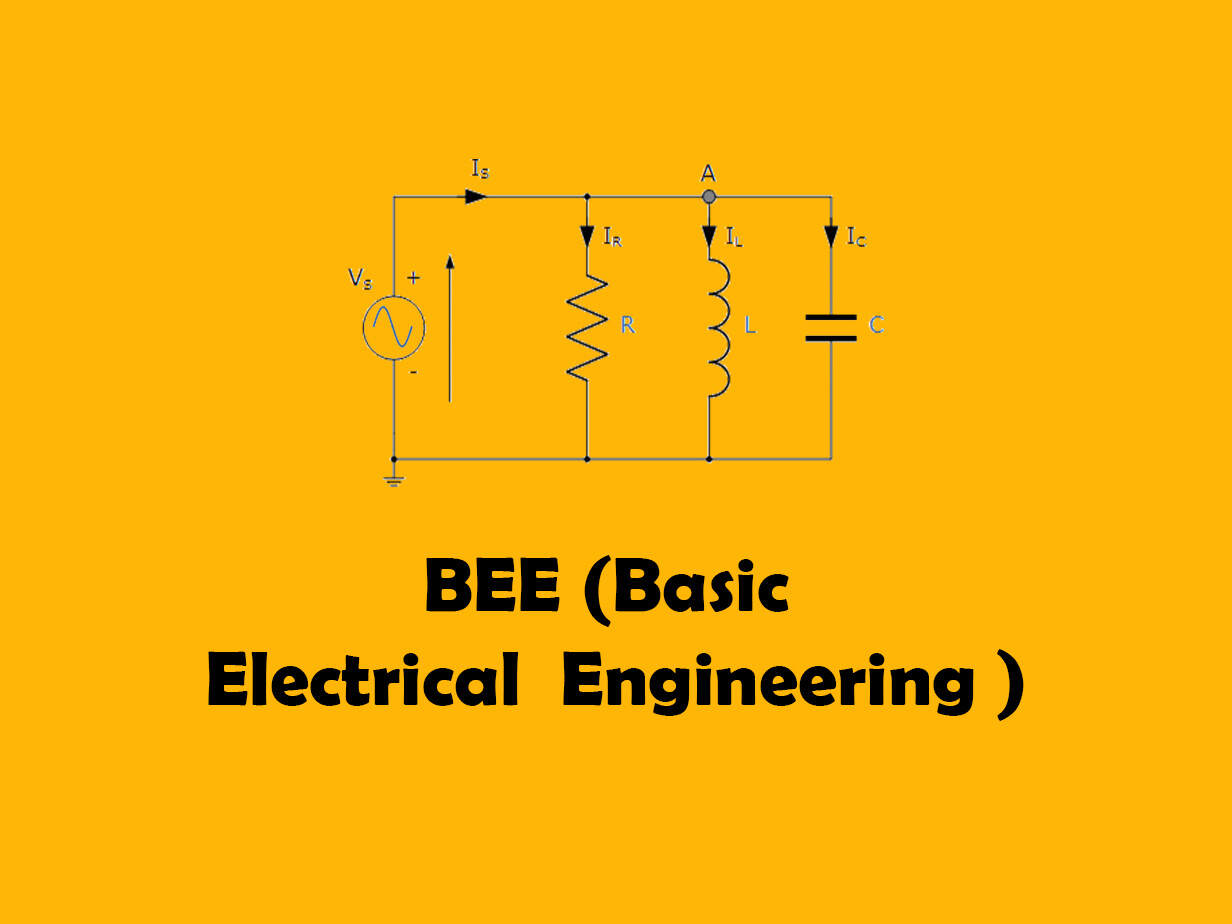
DC Circuits
- BEE introduction (voltage , current ,resistance )
- How to add voltage ,current and resistance in series and parallel circuit
- Nodal analysis with solved example
- Nodal analysis of Supernode
- Thevenin theorem with solved examples
- Equivalent resistance problems with solved Examples
- Nortons theorem with solved examples
- Superposition Theorem with solved example
- Source Transformation with solved example
- Superposition Theorem with solved example (part 2 )
- Mesh analysis for SUPERMESH
- Mesh analysis best trick
- Star Delta Introduction
- Delta to star conversion (Easy trick ) Vice versa with solved example
- Numerical Of Star Delta
- Maximum power transfer theorem
-
AC circuit
-
Transformer
-
DC GENERATOR and DC MOTOR
-
HOW TO PASS
-
BEE Viva Questions
-
Module 5
-
Module 6
-
AC Analysis
-
Three phase
- What is a 3-phase Electrical System
- How 3-Phase POWER is Generated
- Line and Phase Quantities
- Single phase v_s Three Phase
- Star Connection-1
- Star Connection-2
- Delta Connection
- Power Calculation in 3_Phase_Circuits
- Numerical on Star Configuration
- Numerical on Delta Configuration
- Star-Delta Transformation-1
- Star-Delta Transformation-2
- Star-Delta Transformation-3
- Numerical on Star-Delta Transformation
- Application of Star-Delta Transformation-1
- Application of Star-Delta Transformation-2
- Basics of Power Measurement
- Two Wattmeter Method-1
- Two Wattmeter Method-2
- Numericals on 2-Wattmeter Method-1
- Numericals on 2-Wattmeter Method-2
BEE (Basic Electrical Engineering)
BEE (Basic Electrical Engineering) is semester 1 subject of final year of computer engineering in Mumbai University. Objectives for the subject Basic Electrical Engineering is to provide knowledge on the fundamentals of D.C. circuits and their applications.
To impart knowledge on fundamentals of A.C. circuits and its applications. To inculcate knowledge on the basic operation and the performance of transformer. To impart knowledge on fundamentals of 3-Phase A.C. circuits and its applications. To provide knowledge on fundamentals of DC machines. Outcomes for the subject Basic Electrical Engineering is that Learner will be able to evaluate D.C. circuits using network theorems. To evaluate 1-Phase AC circuits. To illustrate constructional features and operation of 1-Phase transformer. To evaluate 3-phase AC circuits. To illustrate working principle of DC machines. To conduct experiments on D.C. circuits and AC circuits.
Direct current (DC) is the one directional flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors, insulators, or even through a vacuum as in electron or ion beams. The electric current flows in a constant direction, distinguishing it from alternating current (AC). A term formerly used for this type of current was galvanic current. Alternating current (AC) is an electric current which periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time in contrast to direct current (DC) which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in which electric power is delivered to businesses and residences, and it is the form of electrical energy that consumers typically use when they plug kitchen appliances, televisions, fans and electric lamps into a wall socket. A common source of DC power is a battery cell in a flashlight. The abbreviations AC and DC are often used to mean simply alternating and direct, as when they modify current or voltage. The usual waveform of alternating current in most electric power circuits is a sine wave, whose positive half-period corresponds with positive direction of the current and vice versa. In certain applications, like guitar amplifiers, different waveforms are used, such as triangular waves or square waves. Audio and radio signals carried on electrical wires are also examples of alternating current. These types of alternating current carry information such as sound (audio) or images (video) sometimes carried by modulation of an AC carrier signal. These currents typically alternate at higher frequencies than those used in power transmission.
Module DC Circuits(Only Independent Sources) consists of the following subtopics Kirchhoff ’s laws, Ideal and practical voltage and current source, Mesh and Nodal analysis, Super node and Super mesh analysis, Source transformation, Star-delta transformation, Superposition theorem, Thevenin’s theorem, Norton’s theorem, Maximum power transfer theorem, (Source transformation not allowed for Superposition theorem, Mesh and Nodal analysis).Module AC Circuits consists of the following subtopics Generation of alternating voltage and currents, RMS and Average value, form factor, crest factor, AC through resistance, inductance and capacitance, R-L, R-C and R-LC series and parallel circuits, phasor diagrams, power and power factor, series and parallel resonance, Q factor and bandwidth. Module Three Phase Circuits consists of the following subtopics Three phase voltage and current generation, star and delta connections(balanced load only), relationship between phase and line currents and voltages, Phasor diagrams, Basic principle of wattmeter, measurement of power by one and two wattmeter methods. Module Single Phase Transformer consists of the following subtopics Construction, working principle, emf equation, ideal and practical transformer, transformer on no load and on load, phasor diagrams, equivalent circuit, OC and SC test, regulation and efficiency.Module DC Machines consists of the following subtopics Principle of operation of DC motors and DC generators, construction and classification of DC machines, emf equation.
Suggested References books for the subject Basic Electrical Engineering by Mumbai university are as follows B.L.Theraja “Electrical Engineering “ Vol-I and II, S.N.Singh, “Basic Electrical Engineering” PHI , 2011 Book name and author. Suggested Texts books for the subject Basic Electrical Engineering by Mumbai university are as follows V. N. Mittal and Arvind Mittal “Basic Electrical Engineering” Tata McGraw Hill, (Revised 2. Edition). Electrical Engineering Fundamentals” by Vincent Del Toro, PHI Second edition, 2011. Edward Hughes: Electrical and Electrical Technology, Pearson Education (Tenth edition). D P Kothari and I J Nagrath “Theory and Problems of Basic Electrical Engineering”, PHI 13 thedition 2011.
Prepare For Your Placements: https://lastmomenttuitions.com/courses/placement-preparation/
![]()
/ Youtube Channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCGFNZxMqKLsqWERX_N2f08Q
Follow For Latest Updates, Study Tips & More Content!
Course Features
- Lectures 80
- Quizzes 0
- Duration 50 hours
- Skill level All levels
- Language English
- Students 98
- Certificate No
- Assessments Yes



