Get Latest Exam Updates, Free Study materials and Tips
Q1. Define Engineering Drawing. Why Drawing is called the Universal Language of Engineers?
Answer :
Q2. Name Different Drawing Instruments.?
Ans –Drawing board, drawing sheet, mini-drafter, scale, pencil and sandpaper block, cello-tape, eraser and compass
Q3. What are Different Types of Scales?
Ans- Different styles of scales are:
Q4. What are Applications Of Scales?
Ans-Scales can be used for the following purposes:
Q5. What Are The Requirements For The Construction Of A Scale?
Answer :(i) Maximum distance to be measured
(ii) R.F.( representative fraction) of the scale
Units of scale i.e. mm, cm, m, km
Q6. Name The Different Types Of Line Use In Engg. Drawing?
Q7. What Are Standard Specifications Of Drawing Sheets And Pencils?
Ans- A0, A1, A2, A3, A4
H, 2H, 3H, 4H etc
B, 2B, 3B, 4B etc
Q8.What do you Mean by R.F.? What is The Unit of R.F.?
Ans: – The Ratio of length of the drawing to the actual length of the object is called The Representative Fraction (R.F).
R.F. = Drawing Length / Actual Length
R.F is unitless.
Q9. What Do You Mean By Convention/ Code?
Ans: The representation of any matter by some standard sign or symbol on the drawing is known as convention or code. The conventions make the drawing simple and easy to draw.
Q1. What are conic sections and why are they called so?
Ans. Ellipse, parabola and hyperbola are called conic sections because these curves appear on the surface of the cone when it is cut by some typical cutting planes.
Q2. Define Ellipse?
Ans:
Q3.Name the Method to draw an ellipse?
Ans
Q4. Define Parabola?
Ans. It is the locus of a point moving in a plane is such a way that the ratio of its distance from a fixed point is always equal to its distance from a fixed line. In other word its eccentricity is equal to one.
Q5. Name the Method to draw a Parabola ?
Ans
Q6. Define hyperbola?
Ans
Q7. Name the Method to draw a Hyperbola?
Ans
Q8. What is the significance of normal and tangent on a curve?
Ans. When force is applied on any point of the curve, we are more concerned with its two components, perpendicular to the curve and along the curve. That’s why we are interested in normal and tangent of the curve.
Q9. Define Cycloid ?
Ans. It is a locus of a point on the circumference of the circle , which rolls on a straight line , without slipping
Q10. What are Cycloidal Curves?
Ans.
Q11. What is the application of Cycloidal Curves?
Ans. Cycloidal Curves are used in gear teeth profiles.
Q12. What are the applications of conic sections?
Ans.
Q1. Define A Line In General. Also Define It From The Drawing Point Of View?
Ans-
Q2. Define Line, Plane & Solid?
Ans-
Q3. What Is The Trace Of A Line?
Ans- Trace of a line is the point where the line meets the plane on extending the line. If the line is inclined to H.P., it will have a H.T., (horizontal trace).
If the line is inclined to V.P., it will have a V.T., (Vertical trace).
If the line lies in a horizontal plane, it will have a horizontal trace as a line itself.
If the line lies in a vertical plane, it will have a vertical trace as a line itself
Q4. What Do You Mean By H.T & V.T Of A Line & A Plane?
Ans – The Point Where the True Lengths of a Line Inclined To H.P or V.P Will Meet H.P & V.P
When Produced Will Be H.T & V.T Respectively,
Trace of a Lines are Points Where as Traces of Planes Are Lines
Q5. What is the Difference B/W True Inclination of a Line and Apparent Angles?
Ans- The angles which the true length of a line makes with h.p or v.p is true inclination. when a line is inclined to both the planes, its projection are shorter than the true length & inclined to xy at angles greater than the true inclination. these angles viz .alpha & bita are called apparent angles of inclination.
Q6. What is the Difference in The Shape of Trace of a Line & Trace of a Plane?
Ans- The Trace of a Line is a Point; Whereas the trace of a plane is a line.
Q7. What Are Auxiliary Planes? What Is The Use Of Auxiliary Planes?
Ans-Plane Perpendicular To Both The Principal Planes Is Called Auxiliary Plane. Side Views Of The Objects Are Taken On It.
Q8. Name The Principal Planes Of Projection
Ans- The principal planes of projection are three:
Q9. What Is The Most Important Type Of Problems On The Projections Of A Straight Line?
Ans-
There are two main types of problems on the projections of a straight line:
Q10. What do you mean by Oblique Plane ?
Ans-
When a plane surface is inclined to one of the principal plane and a side or a diagonal or diameter of a plane surface is a parallel to that principal plane and inclined to other plane surface will be called oblique plane
Define Oblique Projection
Q1. Define Solid?
Ans-
Q2. What Is Difference B/W Prism and Pyramid.
Ans –
Q3. What Do You Mean By Right & Regular Prism, Pyramid Cone & Cylinder?
Ans-
Right Means Axis Vertical & Perpendicular To Base & Regular Means All Sides Equal.
Q4. What is Difference B/W Cone & Cylinder?
Ans-
Q5. What do mean by Generator Of Cone?
Ans –
Cone Is Made Of Number Of Generator Lines. All The Lines Joining Vertex To The Circular Base Are Generator.
Q6. Differentiates B/W Cube, Cuboid and a Square Prism.
Ans-
Q7. Name The Method Used For Obtaining The Developments Of Prisms & Cylinders.
Ans- Parallel- Line Development Method.
Q8. Name The Methods Used For Obtaining The Development Of Cones & Pyramids.
Ans- Radial- Line Development Method.
Q9. Name The Method Used For Obtaining The Development Of Sphere.
Ans- Approximate Method
Q10. What is Sections of solids and Section Plane.
Ans – SECTIONING A SOLID – An object ( here a solid ) is cut by some imaginary cutting plane to understand internal details of that object. The action of cutting is called SECTIONING a solid & The plane of cutting is called SECTION PLANE.
Q1. Define Orthographic Projection
Ans- Orthographic projection is a means of representing three-dimensional objects in two dimensions. It is a form of parallel projection, in which all the projection lines are orthogonal to the projection plane, resulting in every plane of the scene appearing in affine transformation on the viewing surface.
Q2. Define Elevation, Plan & End View?
Ans-
Q3. What do you mean by First Angle and Third Angle Projection Systems?
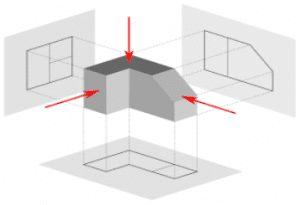 First Angle Projection
First Angle Projection
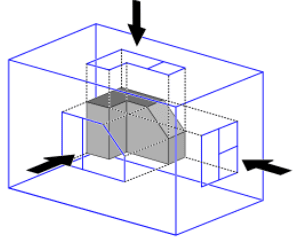 Third Angle Projection
Third Angle Projection
Q4. Why are the Projections of Objects not drawn in the Second and Fourth Angle of Projections?
Ans-The front view and the top view will overlap each other and thus there will be no clarity and it will all be only confusion.
Q1. Define isometric projection
Q2. Differentiates B/W Isometrics Projection And Isometrics View?
Ans- The View Drawn with the True Scale is Called Isometric Drawing Or Isometric View While That Drawn With The Use Of Isometric Scale Is Called Isometric Projection.
Q3. Name the Method Preferred For Drawing Ellipse In Isometric Projection.
Ans – Four Centre Method
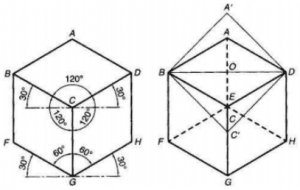
Isometric axes: The Three Lines CB, CD, CG meeting at a point C and making an angle of 1200 with each other are called Isometric axes.
Isometric Lines: The Lines parallel to the Isometric Axis are termed Isometric lines. Example from above fig. AB, AD, GF, GH, BF, DH are Isometric Lines.
Non-Isometric Lines: The lines which are not parallel to the isometric axes are known as NonIsometric Lines Example from above fig. BD, AC, CF, BG are Non-Isometric Lines.
Isometric Planes: The planes representing the faces of the cube as well as other planes parallel to these planes are termed as Isometric Planes Example from above fig. ABCD, BCGF, CGHD are Isometric Planes
Isometric Scale: It is the scale that is used to convert the true length into Isometric Length
Prepare For Your Placements: https://lastmomenttuitions.com/courses/placement-preparation/
![]()
/ Youtube Channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCGFNZxMqKLsqWERX_N2f08Q
Follow For Latest Updates, Study Tips & More Content!
Not a member yet? Register now
Are you a member? Login now